Reliable power keeps operations running. For energy operations managers, selecting the right backup system can mean the difference between smooth performance and costly downtime. In this article, we explain the key differences between genset vs inverter systems, how each works, and how to choose the best option for your facility.
What Is a Genset?
Genset Meaning and Function
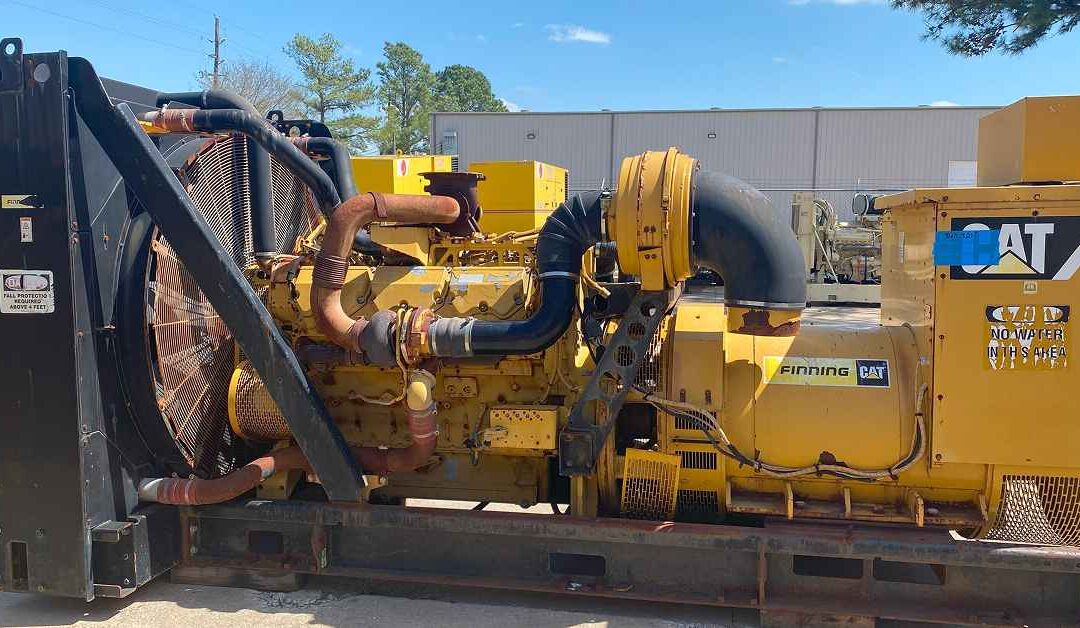
A genset, short for “generator set,” combines an internal combustion engine with an alternator. The engine produces mechanical energy by burning fuel. The alternator then converts that energy into electrical power.
How Genset Works
The engine burns fuel—commonly diesel, natural gas, or propane—to create rotational energy. The alternator uses that motion to generate electricity. Gensets supply alternating current (AC), which powers most industrial and commercial equipment.
Genset Applications
Operations managers often use gensets for:
- Industrial facilities
- Offshore platforms
- Marine vessels
- Hospitals
- Construction sites
- Data centers
At React Power Solutions, we carry new and used gensets from trusted brands like Caterpillar, Cummins, Kohler, Waukesha, and Detroit Diesel, ensuring your operation has a reliable power source.
What Is an Inverter?
Inverter Function and Technology
An inverter converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). Instead of burning fuel directly, inverters draw DC power from batteries, solar panels, or hybrid sources. The internal electronics then create a stable, consistent AC output.
Inverter Applications
Inverters work well for:
- Backup power for offices
- Residential use
- Sensitive electronic equipment
- Portable or temporary setups
- Remote locations using renewable energy
Inverter systems deliver consistent voltage and frequency, making them ideal for equipment sensitive to power fluctuations.
Genset vs Inverter: Key Differences
Both gensets and inverters provide backup power, but they operate differently. Understanding these differences helps you make the right decision for your facility.
Power Output
- Genset: Delivers high power output, suitable for running entire facilities.
- Inverter: Offers moderate power output, best for small-scale or sensitive loads.
Fuel Efficiency
- Genset: Burns fuel continuously, regardless of load size.
- Inverter: Adjusts power output based on demand, using less fuel overall.
Noise
- Genset: Typically louder due to engine operation.
- Inverter: Quieter, with some models producing minimal noise.
Maintenance
- Genset: Requires regular maintenance like oil changes, filter replacements, and engine inspections.
- Inverter: Minimal mechanical maintenance; mainly involves checking battery health and software updates.
Emissions
- Genset: Produces exhaust emissions, especially when using diesel.
- Inverter: Lower emissions, especially when integrated with solar or battery systems.
Portability
- Genset: Often large and stationary.
- Inverter: Compact and easy to transport.
Cost
- Genset: Lower upfront cost but higher operating and maintenance costs.
- Inverter: Higher initial investment but lower long-term costs due to fuel savings and reduced maintenance.
Use Case Scenarios: Genset or Inverter?
When to Choose a Genset
A genset is the better choice when:
- Your facility has high energy demands.
- You need continuous, long-term power.
- Your operation cannot afford downtime.
- You require power for heavy equipment or industrial machinery.
Gensets are common in industries like manufacturing, offshore drilling, and marine shipping. React Power Solutions offers a full range of gensets that meet these demands.
When to Choose an Inverter
An inverter works best when:
- You have sensitive electronics that need stable power.
- You operate in noise-sensitive environments.
- You prioritize fuel efficiency and lower emissions.
- Your power needs are portable or temporary.
- You incorporate renewable energy into your system.
Inverters are common for residential backups, small office buildings, and mobile operations like RVs or remote job sites.
Fuel Considerations for Genset vs Inverter
Genset Fuel Options
- Diesel: Common for industrial gensets; reliable and widely available.
- Natural Gas: Cleaner than diesel; ideal for stationary units with continuous fuel supply.
- Propane: Long shelf life and cleaner burn than diesel.
Inverter Power Sources
- Battery Storage: Charges from the grid or renewable sources.
- Solar Panels: Generates DC power directly from sunlight.
- Hybrid Systems: Combines gensets and renewable sources for maximum flexibility.
Cost Breakdown: Genset vs Inverter
Genset Costs
- Lower purchase price.
- Higher fuel and maintenance costs.
- Long-term costs depend on usage hours and fuel prices.
Inverter Costs
- Higher upfront cost.
- Lower operating and maintenance expenses.
- Savings increase over time, especially with renewable integration.
Maintenance Needs: Genset vs Inverter
Genset Maintenance
Gensets require:
- Oil and filter changes
- Fuel system inspections
- Cooling system maintenance
- Exhaust and emissions system checks
Neglecting maintenance increases failure risk and shortens equipment life.
Inverter Maintenance
Inverters require:
- Occasional software updates
- Battery condition monitoring
- Airflow and component inspections
With fewer moving parts, inverters need less frequent service.
Environmental Impact
Genset Emissions
- Produces greenhouse gases and particulate matter.
- May require additional filtration to meet local regulations.
Inverter Emissions
- Minimal emissions, especially with solar or battery input.
- Supports sustainability goals and reduces carbon footprint.
How React Power Solutions Supports Your Backup Power Needs
At React Power Solutions, we understand every operation has unique requirements. We offer:
- New and used gensets from leading brands.
- Expert consultations to size your system correctly.
- Marine, offshore, and industrial power solutions.
- Certified service and rebuild departments to extend equipment life.
Our large Houston-based inventory is ready for immediate deployment worldwide.
Conclusion
Choosing between a genset vs inverter comes down to your specific operational needs. Gensets offer high output and continuous power for heavy-duty applications. Inverters provide efficient, quiet, and stable power for sensitive or smaller-scale systems.
React Power Solutions can help you evaluate your requirements and select the right equipment for your facility. Contact our experienced team today to explore your backup power options.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a genset?
A genset, or generator set, is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. It combines an internal combustion engine with an alternator. The engine burns fuel, creating mechanical energy, which the alternator converts into AC power. Gensets are often used as a backup power source during a power outage.
How does a genset work?
A genset works by converting mechanical energy into electricity. The engine burns fuel like diesel or natural gas to generate motion. This mechanical energy drives the alternator, which produces AC power used by industrial equipment and electronic devices.
What is an inverter?
An inverter is a device that converts DC power into AC power. It draws DC power from batteries or solar panels, then electronically converts it into stable AC electricity. Inverters are often used to power sensitive electronic devices because they deliver clean, consistent electricity.
What is the difference between inverters and generators?
The main difference in the generator vs inverter comparison is how each produces electricity. A genset burns fuel to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. An inverter converts stored DC power into AC power without burning fuel directly. Gensets deliver higher output for heavy equipment, while inverters provide quiet, fuel-efficient power for smaller or sensitive loads.
Which type of generator is better for industrial use?
For high-demand industrial use, a genset is often the better type of generator. It can deliver continuous, high-output power, making it ideal for heavy machinery, data centers, and critical infrastructure. Inverters work well for smaller operations needing stable, efficient backup power for sensitive electronics.
Can inverters run during a power outage?
Yes. Inverters are commonly used as backup power during a power outage. They draw energy from charged batteries or solar panels and convert DC to AC power, keeping electronic devices and essential electrical devices running without engine noise or fuel emissions.
Are inverters better for sensitive electronic devices?
Yes. Inverters produce clean, stable AC power with minimal harmonic distortion. This makes them ideal for sensitive electronic devices such as computers, medical equipment, and communication systems. Conventional generators may produce power fluctuations that can damage these devices.
Is a genset portable?
Many gensets are large and stationary, but some portable power station models exist for smaller-scale applications. Inverters, on the other hand, are generally more compact and lightweight, making them easier to transport for mobile or temporary operations.
How do solar panels work with inverters?
Solar panels generate DC power from sunlight. Inverters convert that DC power into AC power for use by most electrical devices. This combination creates a clean, renewable source of electricity that reduces fuel costs and emissions.
What kind of maintenance do gensets and inverters need?
Gensets require regular maintenance like oil changes, air filter replacements, and fuel system inspections to ensure reliable backup power. Inverters require less maintenance, mainly involving battery checks and occasional software updates.
Can I combine a genset and inverter?
Yes. Many facilities use a hybrid system. The genset handles high power loads or extended outages, while the inverter supplies efficient backup power for sensitive electronic devices or low-demand periods. This combination maximizes reliability and fuel efficiency.