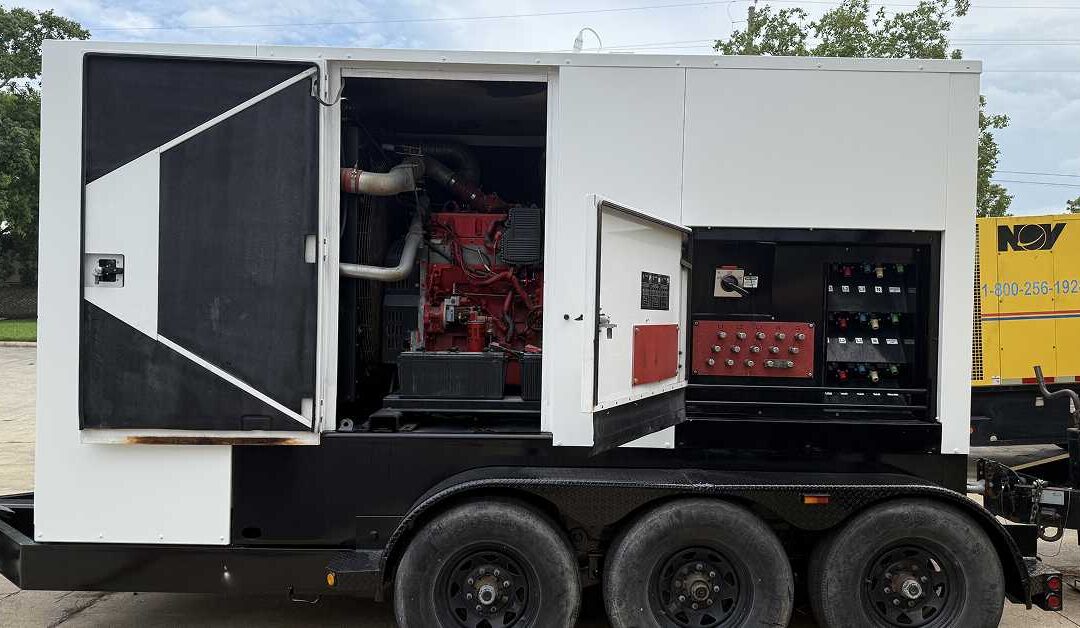
Industrial diesel generators provide reliable power for critical operations across industries, from small manufacturing shops to large-scale data centers. Choosing the right kilowatt (KW) capacity is essential for ensuring continuity, safety, and efficiency. This guide outlines generator applications across different KW ranges, with examples of how businesses apply them in real-world settings.
Small-Scale Industrial Applications (20–100 KW)
Manufacturing Facilities
Small and mid-sized manufacturers depend on generators in the 20–100 KW range to protect essential equipment during outages. Machines such as CNC tools, conveyors, and testing instruments require steady power to avoid production delays or material loss. For instance, a 50–75 KW generator can keep an automotive parts workshop or textile plant running without disruption.
Retail and Commercial Buildings
Shops, restaurants, and office buildings rely on diesel generators in this range to power lighting, elevators, refrigeration, and fire safety systems. A grocery store may use a 60–80 KW unit to maintain refrigeration and checkout systems, preventing spoilage and revenue loss during blackouts.
Telecommunications Infrastructure
Cell towers and small telecom hubs require uninterrupted service. Generators in the 25–50 KW range provide stable backup power, often with automatic start features, ensuring continuous connectivity during extended grid failures.
Medium-Scale Industrial Applications (100–500 KW)
Mid-Size Manufacturing Plants
Facilities with multiple production lines and climate-controlled operations often need 200–300 KW capacity. For example, a food processing plant can rely on this range to support refrigeration, packaging, and safety systems. Stable power quality is critical for protecting sensitive electronic controls.
Healthcare Facilities
Hospitals and medical centers require dependable power for operating rooms, imaging equipment, ICUs, and building systems. A 250–400 KW generator provides sufficient backup while supporting redundancy and seamless power transfer to protect patient care.
Data Centers
Small and medium-sized data centers typically use generators in the 150–400 KW range to power servers, cooling, and networking infrastructure. Even brief outages can cause data loss, so facilities often deploy multiple units for redundancy.
Water Treatment Plants
Municipal plants need reliable power for pumping stations, treatment processes, and controls. A 300 KW generator can sustain wastewater treatment operations, supporting compliance and public health.
Large-Scale Industrial Applications (500–1500 KW)
Major Manufacturing Complexes
Heavy industries such as steel, chemical, and automotive manufacturing often rely on 750–1000 KW generators. These units support process controls, safety systems, and critical machinery, usually integrated into custom electrical setups.
Large Healthcare Campuses
Medical campuses with multiple buildings require 600–1200 KW generators to maintain power across facilities. These systems must handle diverse load demands and often operate in parallel to ensure redundancy.
Commercial High-Rises
Hotels, mixed-use towers, and office buildings depend on 700–1000 KW systems to maintain elevators, life safety systems, and emergency lighting. For example, a 50-story office tower may require an 800 KW generator to support safe evacuation and continuity of services.
Large Data Centers
Enterprise data centers often require 750–1500 KW capacity to support thousands of servers, large-scale cooling systems, and extensive networking infrastructure. Operators such as Google and Amazon deploy multiple megawatt-scale generators configured in parallel to maximize uptime.
Heavy Industrial Applications (1500+ KW)
Utility Power Support
Utilities use 1500+ KW generators for peaking and backup during demand surges or outages. A 2–3 MW system can temporarily power a small community or industrial hub.
Mining Operations
Remote mining facilities rely on 2–5 MW generators as a primary power source. These units drive crushing systems, conveyor networks, and ore processing while meeting long runtime demands.
Petrochemical Facilities
Oil refineries and chemical plants often use 2–10 MW systems to maintain safe operations and emergency shutdown protocols. These generators ensure process safety, fire suppression, and environmental control during power failures.
Marine Applications
Ships, offshore rigs, and cruise vessels use 2–20 MW generators for propulsion and operations. These units must withstand variable loads and harsh environments while supporting crew and passenger safety.
Key Selection Considerations
-
Load Analysis: Account for starting currents, load diversity, and power factor. Many industrial motors require 3–5 times their running current during startup.
-
Runtime Requirements: Determine expected runtime. Grocery operations may need 8–12 hours, while hospitals often require 72+ hours with refueling options.
-
Environmental Conditions: Select generators with proper cooling, enclosures, and protection for high heat, humidity, altitude, or seismic exposure.
-
Integration and Controls: Modern systems integrate with building management, enable remote monitoring, and support automatic paralleling with utility or other generators.
Ensuring Reliable Power with the Right Industrial Diesel Generator
Industrial diesel generators are vital for business continuity, safety, and operational resilience. From 50 KW units in small workshops to 10+ MW systems in petrochemical plants, proper sizing and design ensure reliable performance.
The most effective generator strategy combines:
-
Precise load analysis
-
Adequate capacity with safety margins
-
Integration with existing infrastructure
-
Expert installation and maintenance
Partnering with an experienced provider like React Power Solutions ensures access to engineering expertise, high-performance generator systems, and long-term reliability.