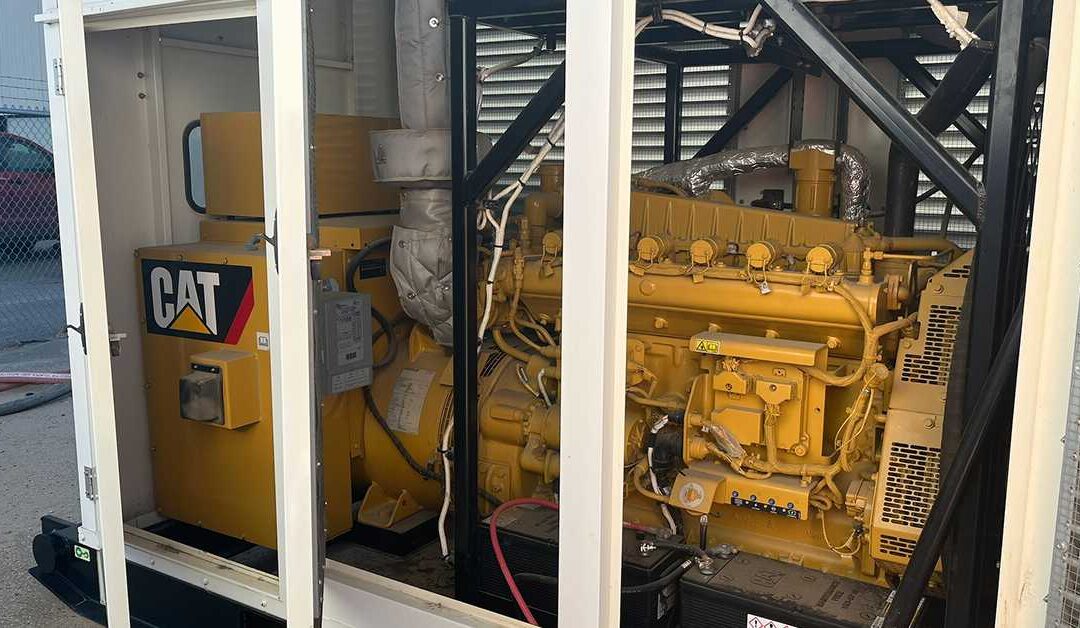
Reliable backup power is essential for hospitals, data centers, and other critical infrastructure. However, meeting emissions standards is just as important as meeting load requirements. Operating non-compliant equipment can lead to penalties, shipment delays, and service interruptions. This guide explains global generator emissions regulations and the technologies that help you meet them.
Why Emissions Compliance Matters for Critical Infrastructure
Operational Impact
Hospitals and data centers require uninterrupted power. If a generator fails compliance checks, it can be taken out of service, risking critical operations. Non-compliance can also delay international shipments, which is costly for time-sensitive projects.
Legal and Financial Risks
Regulatory violations can result in fines, permit revocations, and restrictions on equipment use. This is especially true in regions with strict environmental oversight, such as California or the European Union.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Generator emissions contribute to air pollution. Controlling pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and carbon monoxide (CO) helps protect public health and reduces environmental impact.
Key Pollutants from Generators
-
Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): Contribute to smog and acid rain; can aggravate respiratory conditions.
-
Particulate Matter (PM): Includes soot and microscopic solids that can cause lung and heart problems.
-
Carbon Monoxide (CO): A colorless, odorless gas that can be deadly in enclosed spaces.
-
Hydrocarbons (HC): React with NOx to form ground-level ozone.
-
Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂): Produced from high-sulfur fuels; linked to acid rain.
Global Regulatory Frameworks
United States – EPA Tier Standards
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) sets emissions limits for non-road diesel generators.
-
Tier 1–4 Final: Tier 4 Final is the strictest, requiring advanced emissions controls.
-
Prime Power Generators: Must meet Tier 4 Final standards.
-
Standby/Emergency Generators: Typically follow Tier 2 or Tier 3, with hour limits.
-
State Rules: California’s Air Resources Board (CARB) enforces stricter limits, often exceeding federal rules.
European Union – Stage V Standards
EU Stage V rules align closely with EPA Tier 4 Final but introduce additional particle number (PN) limits for ultra-fine particles. Stage V compliance is required for most new non-road mobile machinery, including portable and rental generators.
International Maritime Organization (IMO)
For marine-based operations, the IMO sets Tier I, II, and III limits for nitrogen oxide emissions. Offshore facilities, floating hospitals, and ships with onboard generators must comply based on the vessel’s build date and operating region.
Other Regional Standards
Many countries follow EPA or EU frameworks but add their own requirements. Exporting generators to regions such as the Middle East or Asia-Pacific requires checking local import and operation rules.
Compliance Technologies and Methods
| Generator Type | Primary Use | Typical Standard | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prime Power | Continuous operation | Tier 4 Final / Stage V | Stricter controls due to high annual run hours |
| Standby / Emergency | Backup use only | Tier 2 or Tier 3 | Extra limits may apply if exceeding 100 hours/year |
| Portable / Mobile | Temporary or rental power | Tier 4 Final / Stage V | Must meet destination country rules |
Engine and Exhaust Treatment Systems
-
Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF): Trap soot and burn it off during regeneration cycles.
-
Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR): Uses urea injection to reduce NOx emissions.
-
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR): Recirculates cooled exhaust to lower combustion temperatures and NOx production.
-
Diesel Oxidation Catalysts (DOC): Reduce HC and CO emissions.
Fuel and Combustion Controls
-
Ultra-Low Sulfur Diesel (ULSD): Reduces sulfur dioxide and protects exhaust after-treatment devices.
-
Electronic Control Modules (ECM): Adjust injection timing, fuel mix, and other parameters for cleaner combustion.
Alternative Power and Hybrid Solutions
-
Natural Gas and LNG Generators: Produce fewer particulates and NOx than diesel.
-
Hybrid Systems: Combine diesel with solar panels or battery storage to reduce run time and emissions.
Compliance Requirements by Application
Best Practices for Ensuring Global Compliance
-
Verify Standards Early: Confirm EPA, EU, IMO, and local rules before purchase.
-
Select Certified Equipment: Choose generators with compliance documentation for multiple regions.
-
Maintain Records: Keep emissions test results, permits, and certification on file.
-
Follow Maintenance Schedules: Service emission control systems as recommended.
-
Train Operators: Ensure staff understand operational limits and proper fueling practices.
-
Consult Experts: Work with suppliers who have compliance experience in your target regions.
How React Power Solutions Supports Compliance
At React Power Solutions, we stock Tier 2, Tier 3, Tier 4 Final, and Stage V generators from leading brands like Caterpillar, Cummins, Kohler, and Waukesha. Our team understands global compliance requirements and helps match the right equipment to your operational and regulatory needs.
-
Industrial, Marine, and Offshore Units: Built and tested for demanding applications.
-
Service and Rebuild Capabilities: Extend equipment life while maintaining emissions compliance.
-
Export Expertise: Guidance on documentation, shipping, and destination country approvals.
-
Immediate Availability: Large inventory ready for deployment worldwide.
Stay Compliant With Tested Inventory
Emissions compliance is essential for safe, legal, and reliable generator operation, especially in critical facilities like hospitals and data centers. By selecting compliant equipment, using the right technologies, and following maintenance best practices, you can meet EPA, EU, and IMO standards anywhere in the world.
React Power Solutions is ready to help you find a generator that meets your load requirements and your compliance obligations—whether your project is across town or across the globe.